一、冒泡排序:
1、算法思想:
对要排序的数据,从上到下依次比较两个相邻的数并加以调整,将最大的数向下移动,较小的数向上冒起。即:每一趟依次比较相邻的两个数据元素,将较小的数放在左边,循环进行同样的操作,直到全部待排序的数据元素排完。
2、实例分析:
例如:我们要将身高不等的十个人站在一排,要求他们按照身高由低到高排队,设将10个人编号为0—9 ,相邻的两个人依次比较,如果左边的比右边的人高,则交换两个人的位置,否则不交换,直到最后两个人,即此时完成了一趟排序。一趟排序后,最高的人已经在最右边了。
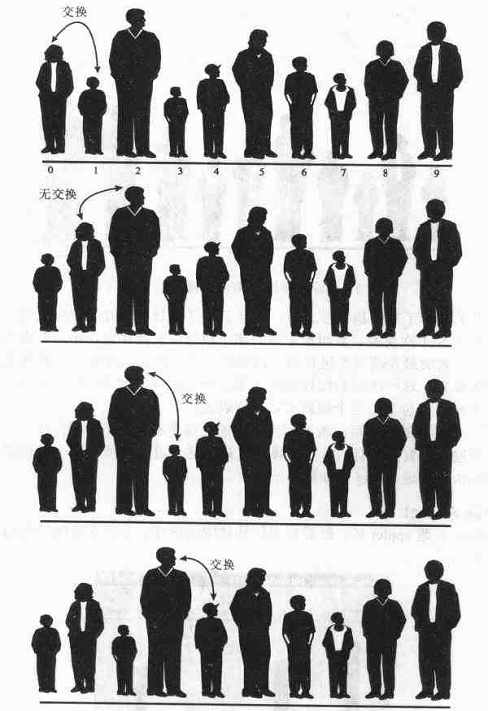
一趟排序后的结果:(将最高者一趟排序后移动到最后位置)
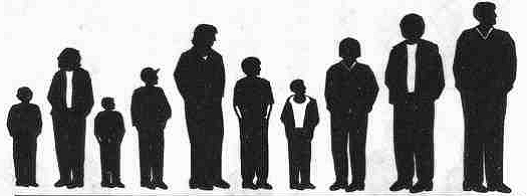
如此都多趟的排序,最终就完成了整个的排序。
3、算法分析:(有小到大排序)
1>、每一趟过程中,就是依次比较两个相邻的数,若a[i]>a[i+1],则交换两数,否则不换;
2>、每一趟就是一重循环,而由于要经过多趟过程,即外面还有一重循环,所以就存在双重循环。
4、算法代码:(Java版)
- /**
- * 冒泡排序 算法
- * @author xcbeyond
- *
- */
- public class BubbleSort {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- int a[] ={13,15,37,89,60,39,12,109,56,72} ;
- int i = 0;
- int j = 0;
- for(i=0;i<10;i++)
- System.out.print(a[i]+” “);
- System.out.println();
- for(i=0;i<a.length;i++)
- for(j=0;j<a.length-i-1;j++)
- {
- if(a[j]>a[j+1])
- {
- int temp;
- temp=a[j];
- a[j]=a[j+1];
- a[j+1]=temp;
- }
- }
- for(i=0;i<10;i++)
- System.out.print(a[i]+” “);
- }
- }
二、选择排序
1、算法思想:
将待排序序列分为两部分,一部分为有序序列,另一部分为无序序列。第一趟:从a[0]到a[n-1]中找到最小的数a[i],然后将a[i]与a[0]交换,第二趟:从a[1]到a[n-1]中找到最小的数a[j],然后将a[j]与a[1]交换,第三趟:从a[2]到a[n-1]中找到最小的数a[k],然后将a[k]与a[2]交换 ……
2、实例分析:
{13,15,37,89,60,39,12,109,56,72}
第一趟 :12 {15,37,89,60,39,13,109,56,72}
第二趟:12 ,13 {37,89,60,39,15,109,56,72}
第三趟:12 ,13 ,15 {89,60,39,37,109,56,72}
……
3、算法代码:
- /**
- * 选择排序
- * @author xcbeyond
- *
- */
- public class SelectSort {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- int a[] ={13,15,37,89,60,39,12,109,56,72} ;
- int i;
- int j;
- for(i = 0;i<a.length;i++)
- System.out.print(a[i]+” “);
- System.out.println();
- for(i = 0;i<a.length;i++){
- int min = a[i];
- for(j = i+1;j<a.length;j++){
- if(min>a[j]){
- int temp;
- temp = min;
- min = a[j];
- a[j] = temp;
- }
- }
- a[i] = min;
- }
- for(i = 0;i<a.length;i++)
- System.out.print(a[i]+” “);
- }
- }
三、插入排序
1、算法思想:
1〉从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为已经被排序
2〉取出第一个未排序元素存放在临时变量temp中,在已经排序的元素序列中从后往前扫描,逐一比较
3〉如果temp小于已排序元素,将该元素移到下个位置
4〉重复步骤3〉,直到找到已排序的元素小于或者等于
2、实例分析:
{13,15,37,89,60,39,12,109,56,72}
第一趟: 13 {15,37,89,60,39,12,109,56,72} temp = 15
temp>13
第二趟: 13 ,15 { 37,89,60,39,12,109,56,72} temp = 37
temp>15 temp>13
第三趟: 13,15 ,37 {89,60,39,12,109,56,72} temp = 89
temp>37 temp>15 temp>13
第三趟: 13,15 ,37 ,89 {60,39,12,109,56,72} temp =60
temp< 89:60<->89 13,15 ,37 , 60,89 {39,12,109,56,72}
temp>37 temp>15 temp>13
第四趟: 13,15 ,37 , 60,89 {39,12,109,56,72} temp = 39
temp<89: 39<->89 13,15 ,37 , 60,39,89 {12,109,56,72}
temp<60 : 39<->60 13,15 ,37 , 39,60,89 {12,109,56,72}
temp>37 temp>15 temp >13
第五趟: 13,15 ,37 , 39,60,89 {12,109,56,72} temp = 12
temp<89 :12<->89 13,15 ,37 ,39,60, 12,89 {109,56,72}
temp<60:12<->60 13,15 ,37 ,39,12,60,89 {109,56,72}
temp<39 :12<->39 13,15 ,37 ,12,39,60,89 {109,56,72}
temp<37 :12<->37 13,15 ,12 ,37 ,39,60,89 {109,56,72}
temp<15: 12<->15 13,12,15 ,37 ,39,60,89 {109,56,72}
temp<13 :12<->13 12,13,15 ,37 ,39,60,89 {109,56,72}
第六趟: 12,13,15 ,37 ,39,60,89 {109,56,72} temp = 109
……
3、算法代码:
- import java.util.Arrays;
- /**
- * 插入排序
- * @author xcbeyond
- *
- */
- public class InsertSort {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- int a[] ={13,15,37,89,60,39,12,109,56,72} ;
- a = insertSort(a);
- String s = Arrays.toString(a);
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- public static int[] insertSort(int[] ary){
- for(int i = 1;i < ary.length;i++){
- int temp = ary[i];
- int j;
- for(j = i-1;j>=0 && temp < ary[j];j–){
- ary[j+1] = ary[j];
- }
- ary[j+1] = temp;
- }
- return ary;
- }
- }
- import java.util.Arrays;
- /**
- * 插入排序
- * @author xcbeyond
- *
- */
- public class InsertSort {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- int a[] ={13,15,37,89,60,39,12,109,56,72} ;
- a = insertSort(a);
- String s = Arrays.toString(a);
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- public static int[] insertSort(int[] ary){
- for(int i = 1;i < ary.length;i++){
- int temp = ary[i];
- int j;
- for(j = i-1;j>=0;j–){
- if(temp < ary[j]){
- ary[j+1] = ary[j];
- }
- else
- break; //找到插入位置
- }
- ary[j+1] = temp;
- }
- return ary;
- }
- }